BMW Developing Steam Assist Drive Based on Waste Heat Recovery
Green Car Congress, December 2005, Niko Horster
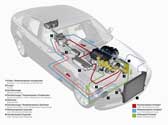
The BMW Research and Engineering group is developing the Turbosteamer -- a steam based auxiliary drive based on principles that are similar to a steam engine. The initial version developed in 2005 used heated fluid in two circuits which were used to boost power to the engine by 15%. The primary energy comes from a high temperature circuit that recovers exhaust heat from the internal combustion engine (routed through the heat exchangers) and conducts via an expansion unit linked to the crankshaft of the internal combustion engine. Much of the remaining heat is absorbed by the cooling circuit of the engine, which is the secondary energy supply for the Turbosteamer. BMW engineers estimated that more than 80% of the heat of the exhaust gas was recycled, but they have been working on making the components simpler, and easier to fit (or retrofit) into the current series of BMW engines, and update on their progress was posted in 2011 BMW provides an update on waste heat recovery projects; Turbosteamer and the Thermoelectric Generator
Gizmag has a additional pictures and a better write-up of the process: http://www.gizmag.com/go/4936/
And BMW's Press release Looking for the next gram